- All Implemented Interfaces:
Cloneable
- Java is a runtime environment maintained by Oracle that you must install on your Mac to be able to run applications written using the Java programming language. Moreover, Java allows developers to make apps available on multiple operating systems at the same time because Java-based utilities.
- Install Oracle Java 7 on Mac OS X. Nowadays, just about everything on the web uses Java. At some point or another you will probably need to install Java on Mac OS X to be able to enjoy the Internet, websites and Apps to their fullest.
Download Java for (x64) File Info. The file comes from the official site java.com digitally signed by Oracle Americe Inc. Check file with all antiviruses Virustotal.com. I have another OS. JDK 14.0.2 General-Availability Release. This page provides production-ready open-source builds of the Java Development Kit, version 14, an implementation of the Java SE 14 Platform under the GNU General Public License, version 2, with the Classpath Exception. Commercial builds of JDK 14.0.2 from Oracle, under a non-open-source license, can be found at the Oracle Technology Network.
A MAC provides a way to check the integrity of information transmitted over or stored in an unreliable medium, based on a secret key. Typically, message authentication codes are used between two parties that share a secret key in order to validate information transmitted between these parties.
A MAC mechanism that is based on cryptographic hash functions is referred to as HMAC. HMAC can be used with any cryptographic hash function, e.g., SHA256 or SHA384, in combination with a secret shared key. HMAC is specified in RFC 2104.
Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard Mac algorithms:
HmacSHA1HmacSHA256
- Since:
- 1.4
Constructor Summary
Constructors Modifier Constructor Description protectedMac(MacSpi macSpi,Provider provider,String algorithm)Method Summary
Modifier and Type Method Description Objectclone()Returns a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.byte[]doFinal()byte[]doFinal(byte[] input)Processes the given array of bytes and finishes the MAC operation.voiddoFinal(byte[] output,int outOffset)StringgetAlgorithm()Returns the algorithm name of thisMacobject.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm,String provider)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.static MacgetInstance(String algorithm,Provider provider)Returns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.intgetMacLength()ProvidergetProvider()Returns the provider of thisMacobject.voidinit(Key key)voidinit(Key key,AlgorithmParameterSpec params)Initializes thisMacobject with the given key and algorithm parameters.voidreset()voidupdate(byte input)Processes the given byte.voidupdate(byte[] input)voidupdate(byte[] input,int offset,int len)Processes the firstlenbytes ininput, starting atoffsetinclusive.voidupdate(ByteBuffer input)Processesinput.remaining()bytes in the ByteBufferinput, starting atinput.position().Methods declared in class java.lang.Object
equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait
Constructor Details
Mac
protectedMac(MacSpi macSpi,Provider provider,String algorithm)- Parameters:
macSpi- the delegateprovider- the provideralgorithm- the algorithm
Method Details
getAlgorithm
public finalStringgetAlgorithm()Returns the algorithm name of thisMacobject.This is the same name that was specified in one of the
getInstancecalls that created thisMacobject.- Returns:
- the algorithm name of this
Macobject.
getInstance
public static finalMacgetInstance(String algorithm) throws NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionReturns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.This method traverses the list of registered security Providers, starting with the most preferred Provider. A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the first Provider that supports the specified algorithm is returned.
Note that the list of registered providers may be retrieved via the
Security.getProviders()method.- Implementation Note:
- The JDK Reference Implementation additionally uses the
jdk.security.provider.preferredSecurityproperty to determine the preferred provider order for the specified algorithm. This may be different than the order of providers returned bySecurity.getProviders(). - Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Security Standard Algorithm Names Specification for information about standard algorithm names.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject - Throws:
NoSuchAlgorithmException- if noProvidersupports aMacSpiimplementation for the specified algorithmNullPointerException- ifalgorithmisnull- See Also:
Provider
getInstance
public static finalMacgetInstance(String algorithm,String provider) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException,NoSuchProviderExceptionReturns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the specified provider is returned. The specified provider must be registered in the security provider list.
Note that the list of registered providers may be retrieved via the
Security.getProviders()method.- Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Security Standard Algorithm Names Specification for information about standard algorithm names.provider- the name of the provider.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject - Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if theproviderisnullor emptyNoSuchAlgorithmException- if aMacSpiimplementation for the specified algorithm is not available from the specified providerNoSuchProviderException- if the specified provider is not registered in the security provider listNullPointerException- ifalgorithmisnull- See Also:
Provider
getInstance
public static finalMacgetInstance(String algorithm,Provider provider) throws NoSuchAlgorithmExceptionReturns aMacobject that implements the specified MAC algorithm.A new Mac object encapsulating the MacSpi implementation from the specified Provider object is returned. Note that the specified Provider object does not have to be registered in the provider list.
- Parameters:
algorithm- the standard name of the requested MAC algorithm. See the Mac section in the Java Security Standard Algorithm Names Specification for information about standard algorithm names.provider- the provider.- Returns:
- the new
Macobject - Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if theproviderisnullNoSuchAlgorithmException- if aMacSpiimplementation for the specified algorithm is not available from the specifiedProviderobjectNullPointerException- ifalgorithmisnull- See Also:
Provider
getProvider
Returns the provider of thisMacobject.- Returns:
- the provider of this
Macobject.
getMacLength
Returns the length of the MAC in bytes.- Returns:
- the MAC length in bytes.
init
public finalvoidinit(Key key) throws InvalidKeyException- Parameters:
key- the key.- Throws:
InvalidKeyException- if the given key is inappropriate for initializing this MAC.
init
public finalvoidinit(Key key,AlgorithmParameterSpec params) throws InvalidKeyException,InvalidAlgorithmParameterExceptionInitializes thisMacobject with the given key and algorithm parameters.- Parameters:
key- the key.params- the algorithm parameters.- Throws:
InvalidKeyException- if the given key is inappropriate for initializing this MAC.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException- if the given algorithm parameters are inappropriate for this MAC.
update
public finalvoidupdate(byte input) throws IllegalStateException- Parameters:
input- the input byte to be processed.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
public finalvoidupdate(byte[] input) throws IllegalStateException- Parameters:
input- the array of bytes to be processed.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
public finalvoidupdate(byte[] input,int offset,int len) throws IllegalStateExceptionProcesses the firstlenbytes ininput, starting atoffsetinclusive.- Parameters:
input- the input buffer.offset- the offset ininputwhere the input starts.len- the number of bytes to process.- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
update
Processesinput.remaining()bytes in the ByteBufferinput, starting atinput.position(). Upon return, the buffer's position will be equal to its limit; its limit will not have changed.- Parameters:
input- the ByteBuffer- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.- Since:
- 1.5
doFinal
public finalbyte[]doFinal() throws IllegalStateExceptionFinishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).- Returns:
- the MAC result.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
doFinal
public finalvoiddoFinal(byte[] output,int outOffset) throws ShortBufferException,IllegalStateExceptionFinishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).The MAC result is stored in
output, starting atoutOffsetinclusive.- Parameters:
output- the buffer where the MAC result is storedoutOffset- the offset inoutputwhere the MAC is stored- Throws:
ShortBufferException- if the given output buffer is too small to hold the resultIllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
doFinal
public finalbyte[]doFinal(byte[] input) throws IllegalStateExceptionProcesses the given array of bytes and finishes the MAC operation.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).- Parameters:
input- data in bytes- Returns:
- the MAC result.
- Throws:
IllegalStateException- if thisMachas not been initialized.
reset
Resets thisMacobject.A call to this method resets this
Macobject to the state it was in when previously initialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec). That is, the object is reset and available to generate another MAC from the same key, if desired, via new calls toupdateanddoFinal. (In order to reuse thisMacobject with a different key, it must be reinitialized via a call toinit(Key)orinit(Key, AlgorithmParameterSpec).clone
public finalObjectclone() throws CloneNotSupportedExceptionReturns a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.- Overrides:
clonein classObject- Returns:
- a clone if the provider implementation is cloneable.
- Throws:
CloneNotSupportedException- if this is called on a delegate that does not supportCloneable.- See Also:
Cloneable
This topic includes the following sections:
System Requirements for Installing the JDK on macOS
The following are the system requirements for installing the JDK on macOS:
Any Intel-based computer running macOS.
Administrator privileges.
You cannot install Java for a single user. Installing the JDK on macOS is performed on a systemwide basis for all users. Administrator privileges are required to install the JDK on macOS.
Determining the Default JDK Version on macOS
When starting a Java application through the command line, the system uses the default JDK.
You can determine which version of the JDK is the default by entering java -version in a Terminal window. If the installed version is 13 Interim 0, Update 0, and Patch 0, then you see a string that includes the text 13. For example:
To run a different version of Java, either specify the full path, or use the java_home tool. For example:
$ /usr/libexec/java_home -v 13 --exec javac -version
Installing the JDK on macOS
- Download the JDK
.dmgfile,jdk-13.interim.update.patch_osx-x64_bin.dmg.Before the file can be downloaded, you must accept the license agreement.
- From either the browser Downloads window or from the file browser, double-click the
.dmgfile to start it.A Finder window appears that contains an icon of an open box and the name of the.pkgfile. - Double-click the
JDK 13.pkgicon to start the installation application.The installation application displays the Introduction window. - Click Continue.
- Click Install. A window appears that displays the message: Installer is trying to install new software. Enter your password to allow this.
- Enter the Administrator user name and password and click Install Software.The software is installed and a confirmation window is displayed.
.dmg file if you want to save disk space. Uninstalling the JDK on macOS
You must have Administrator privileges.Note:
Do not attempt to uninstall Java by removing the Java tools from /usr/bin. This directory is part of the system software and any changes will be reset by Apple the next time that you perform an update of the OS.
- Go to
/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines. - Remove the directory whose name matches the following format by executing the
rmcommand as a root user or by using thesudotool:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-13.interim.update.patch.jdkFor example, to uninstall 13 Interim 0 Update 0 Patch 0:
$ rm -rf jdk-13.jdk
Installation FAQ on macOS Platform
This topic provides answers for the following frequently asked questions about installing JDK on macOS computers.
1. How do I find out which version of Java is the system default?
When you run a Java application from the command line, it uses the default JDK. If you do not develop Java applications, then you do not need to worry about this. See Determining the Default JDK Version on macOS.
2. How do I uninstall Java?
See Uninstalling the JDK on macOS.
3. After installing Java for macOS 2012-006, can I continue to use Apple's Java 6 alongside the macOS JDK for Java 13?
If you want to continue to develop with Java 6 using command-line, then you can modify the startup script for your favorite command environment. For bash, use this:
$ export JAVA_HOME=`/usr/libexec/java_home -v 13`
Oracle Java For Macbook Pro
Some applications use /usr/bin/java to call Java. After installing Java for macOS 2012-006, /usr/bin/java will find the newest JDK installed, and will use that for all of the Java-related command-line tools in /usr/bin. You may need to modify those applications to find Java 6, or contact the developer for a newer version of the application.
Java 8 For Mac
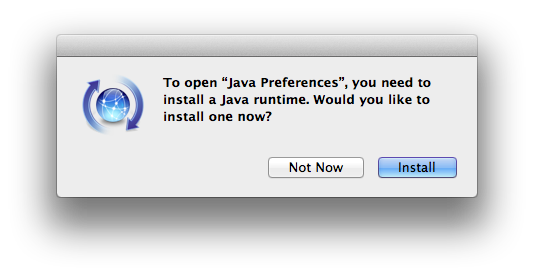
4. What happened to the Java Preferences app in Application Utilities?
The Java Preferences app was part of the Apple Java installation and is not used by Oracle Java. Therefore, macOS releases from Apple that do not include Apple Java will not include Java Preferences.

Comments are closed.